December 3, 2025
Hepatitis B Vaccine Birth Dose for Newborns – Actions for Providers
Public Health continues to recommend that all newborns receive the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of delivery. Additionally, all children should complete the full 3 to 4 dose hepatitis B vaccine series by 18 months of age. Providing the birth dose and completing the series on time offers essential protection during a period of high vulnerability. Delaying vaccination risks missing a crucial window of potential exposure, putting infants at risk for lifelong disease. These recommendations align with the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Recommended Child and Adolescent Immunization Schedule.
Current situation
- The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is expected to vote on changes to the hepatitis B birth dose recommendation at its next meeting, December 4-5, 2025.
- Hepatitis B birth dose remains critical for preventing perinatal transmission and has been tested extensively for safety and efficacy.
- This Health Advisory reinforces key evidence to support immunizing newborns against hepatitis B to prevent cases of perinatally-acquired hepatitis B infections.
Actions requested
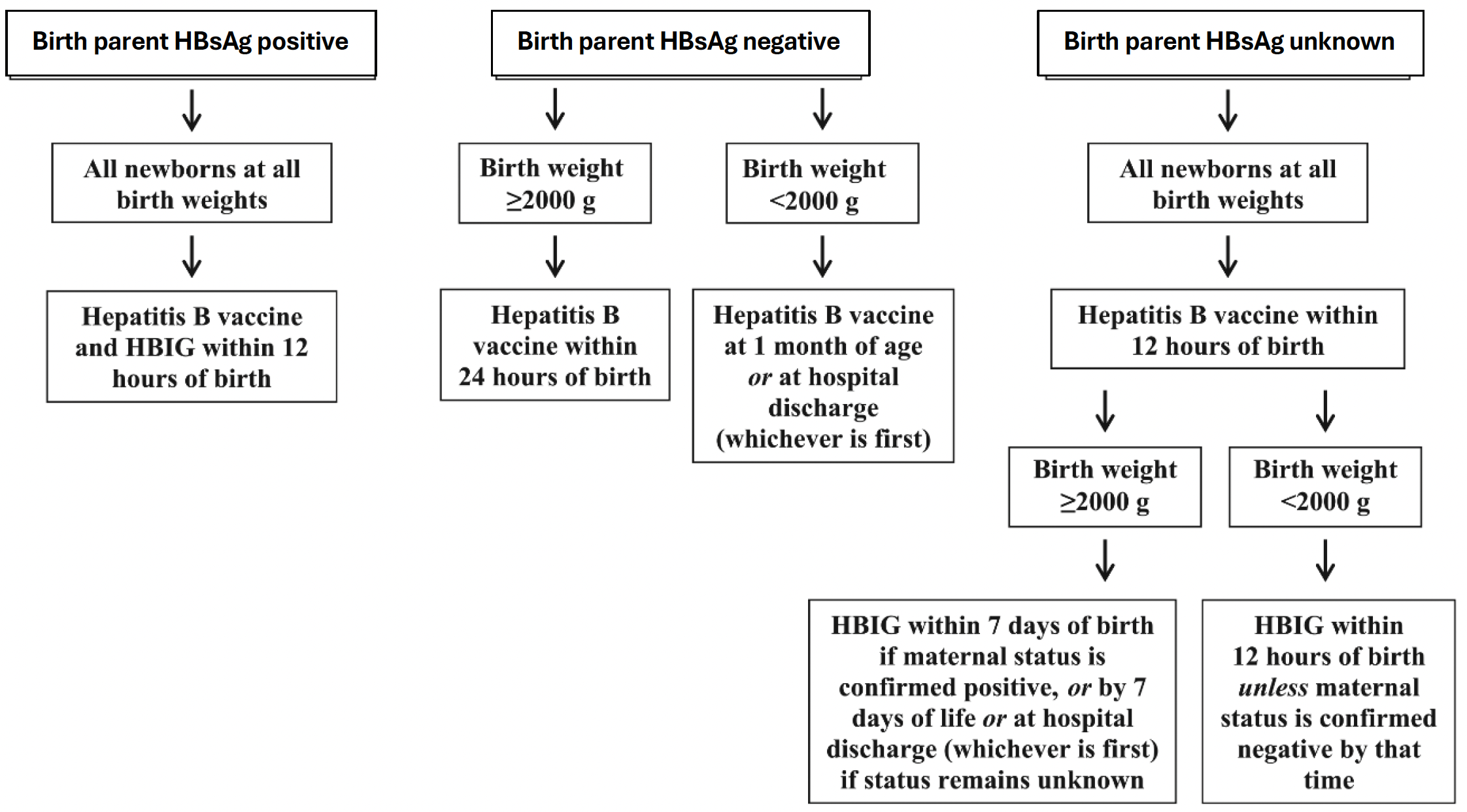
- Continue to administer hepatitis B vaccine to all newborns based on the below flowchart adapted from Elimination of Perinatal Hepatitis B: Providing the First Vaccine Dose Within 24 Hours of Birth, Am. Academy of Pediatrics
- Ensure completion of the 3-4 dose hepatitis B vaccine series by 18 months of age regardless of the birth parents’ hepatitis B infection status.
- For infants born to a parent who is hepatitis B-positive, perform perinatal post-vaccination serologic testing 1-2 months after vaccine series completion, but not before 9 months of age.
Background
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer, and death.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or body fluids, and perinatal exposure typically occurs during labor and delivery.
- Infants can also contract hepatitis B from caregivers, household contacts, and others with known or unknown hepatitis B infection, or from blood-contaminated surfaces and objects.
- Hepatitis B infection is particularly devastating to infants.
- Newborns infected with hepatitis B at birth and infants infected in the first year of life have a 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B which has no cure.
- One in four people infected with hepatitis B virus during childhood die from the disease later in life.
- The CDC and the AAP have recommended hepatitis B vaccination since 1991 for all newborns to protect them from this serious but preventable disease.
- The birth dose recommendation is part of a safety net to protect infants born to someone who is infected with hepatitis B that has gone undiagnosed.
- Since 1991, hepatitis B infections in children and teens have decreased by 99%.
- Newborns respond well to a birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine, and after completing the full 3-4 dose vaccine series, 98% of healthy infants achieve full immunity to the virus that lasts at least 30 years.
- Timely vaccination is essential to reduce the risk of chronic hepatitis B and associated complications.
- Studies have consistently shown the hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective, and severe reactions are rare.
Resources
- Recommended Child and Adolescent Immunization Schedule for Ages 18 Years or Younger, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Hepatitis B: The Disease & Vaccines, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
- Viral Hepatitis in Pregnancy, American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Hepatitis B, WA State Dept. of Health
- Elimination of Perinatal Hepatitis B: Providing the First Vaccine Dose Within 24 Hours of Birth, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Hepatitis B Virus: A Comprehensive Strategy for Eliminating Transmission in the United States Through Universal Childhood Vaccination: Recommendations of the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP)
- Universal Hepatitis B Vaccination at Birth: Safety, Effectiveness, and Public Health Impact, Vaccine Integrity Project
 Translate
Translate