Lake Washington
Introduction
Lake Washington
Lake Washington is the largest of the three major lakes in King County, and the second largest natural lake in the State of Washington. Lake Washington is also one of the best examples in the world of successfully restoring a lake by diverting sewage. It has been extensively studied and monitored by King County and others for decades.
Lake Washington water quality
Human activities have a major influence on water quality, but other seemingly subtle biological activities also have great significance. Lake Washington is an interesting example of how human influences and biological processes can alter water quality.
Water quality monitoring
We continuously monitor Lake Washington's water quality and environmental conditions. Updated readings are published daily.
Learn more about how we monitor Lake Washington
See current water quality data (Lake Washington buoy)
See current weather data (Lake Washington buoy)
Tributary stream water quality data
Find out about the water quality and ecology of the tributary streams that feed into Lake Washington.
Lake Washington recreation
Swim beaches
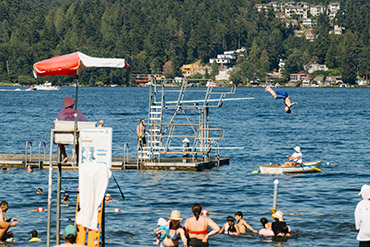
See current information on temperature and water quality of swim beaches on Lake Washington.
Boating

Learn about boating restrictions, equipment requirements, safety, aquatic weed, and other related information. (Washington State marine laws apply to King County boaters.)
Burke-Gilman trail

This trail runs more than 18 miles from Shilshole Bay in the City of Seattle to the City of Bothell where it intersects the Sammamish River Trail.
Scientific reports about Lake Washington
Researchers with the Water and Land Resources Division’s Science Section regularly publish reports, journal articles, and presentations about Lake Washington. Browse our Lake Washington research archive or check out the following highlighted reports:
Estimating toxics loadings to the Lake Washington Watershed
Lake Washington has fish with some of the highest concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) measured across the state. This report answers key questions.
Lake Washington Existing Conditions Report: a report on Lake Washington water quality
Water quality trends and conditions in Lake Washington from 1990 to 2001. Summarizes lake conditions and how Lake Washington has responded to human activities that have changed the watershed.
Sediment Quality Evaluation in Lake Sammamish, Lake Union, and Lake Washington, Washington State
The Sediment Quality Triad (SQT) approach to sediment quality evaluation was used to characterize and assess the extent of altered benthic invertebrate assemblages, sediment contamination and toxicity.
Water Quality Monitoring of Five Mercer Island Drainage Basins from 2008 - 2010
Monitoring results of projects to minimize degraded runoff into Lake Washington, remove silt and control erosion.
Major Lakes Continuous Temperature Study: Interim Progress Report
Aquatic ecosystem responses to changing climate in the three major lakes routinely monitored by King County.
Highway 520 Bridge Storm Water Runoff Study
Part of a comprehensive evaluation of current and future water quality conditions in Lake Washington to support informed decision-making.
Other Lake Washington resources
The Lake Washington Story
A data-driven narrative about Lake Washington, its problems with phosphorus pollution, and factors that affect the lake's water quality.
Greening your shoreline
A tool for lakeshore property owners on Lake Washington and Lake Sammamish to improve shorelines for people and salmon.
Lake Washington Shoreline Master Programs (by jurisdiction)
Drainage basin information
- Cedar River - Lake Washington Watershed
- Cedar River - Lake Washington Watershed map
Drainage map displaying streams, lakes, drainage divides, major roads and cities in the area that drains to Lake Washington and out the Hiram M. Chittenden Locks, except for the Sammamish Watershed area. - Sammamish Watershed
 Translate
Translate